Ethereum 2.0 (“Serenity”) is an update to the Ethereum network that increases speed, efficiency, and scalability, and it will take Ethereum to new heights.
A blockchain that can change the entire crypto space
In technology circles, you can often find fierce discussions on a variety of topics. In recent years, none has been more controversial than the dominance of one blockchain over the rest. From the very advent of cryptocurrencies, the obvious consensus choice was Bitcoin which has been leading the market cap charts since its earliest days.
However, most experts do not expect this to last long. As the progenitor of all cryptocurrencies, the Bitcoin blockchain is beginning to show its age. It suffers from a lot of real limitations, not least because of the inability to scale. In an effort to replace it in the race for dominance, many alternative blockchain implementations have emerged that address some of the inherent problems associated with the Bitcoin network, but so far none of them have managed to capture any significant market segment.
The only notable exception is Ethereum, which has long been the only major competitor to Bitcoin. For its part, although Ethereum is more advanced than Bitcoin, It also suffers from some problems that need to be overcome in order to achieve market dominance. This is exactly what the developers hope to achieve with their upcoming update to the underlying blockchain, which they call Ethereum 2.0.
Refusal from the Proof of Work
One of the reasons why early blockchain implementations (including Bitcoin and Ethereum) suffered from performance problems was that they relied on an energy-intensive processing process known as proof of work (POW) to verify and record transactions. In such a system, participating computer nodes compete to create cryptographic hashes that meet a network-defined level of complexity. To maintain security, this level of complexity is maintained at a high enough level to deter anyone from attacking the network (attack 51), because it would be too expensive to use the necessary hardware.
The problem with proof of work is that it’s terribly inefficient, and it’s done on purpose. To start solving this problem, Ethereum 2.0 is going to transfer its blockchain to a more efficient Proof of stake system. In such a system, the node that records each transaction is selected by an algorithm. Moreover, the probability of selection increases with the amount of currency held by the node owner. This allows you to dramatically reduce the complexity of cryptographic work, which leads to a significant increase in bandwidth for the entire network. Since each node must supply its own currency to participate, an attack on the network would be prohibitively expensive.
It will also fundamentally change the current economy. In fact, the update will completely erase the concept of mining.
As part of another attempt to improve the efficiency and scalability of Ethereum, the upcoming changes will also introduce a processing method known as segmentation. In the current version of the blockchain, all data that are added to the chain must be verified by all participating nodes. This means that the processing speed of the entire system is limited by the speed of its slowest participant. This creates a bottleneck that increases transaction costs and reduces throughput.
By adding segmentation, Ethereum 2.0 can significantly improve resource efficiency. In the new system, this is achieved by dividing data validation tasks between sets of nodes, each of which will be responsible for checking only the received data. This allows the entire block chain to use parallel processing, which can increase the total capacity several times. Between this added technique and the transition to PoS, the new Ethereum blockchain should be much faster and more efficient than its predecessor.
Detailed description of the project
Upon reaching the final upgrade phase, dubbed “phase 2”, Ethereum will achieve its goals of becoming a transparent and open network for decentralized applications and Finance (DeFi).
Eth 2.0 will include sharding to dramatically increase network throughput and reduce gas costs, making it cheaper to send ETH, tokens, and interact with smart contracts. There will also be fundamental economic changes: the upgrade will allow you to support nodes for stacking and earn Ether as passive income.
In many ways, Ethereum 2.0 is a combination of the efforts of thousands of developers who have worked for years. The update will be performed in 3 separate stages, starting from stage 0 (developers count from 0 instead of 1). Over the past few years, Ethereum opponents have often criticized the high transaction costs and fragility of the network during peak usage. Can Eth 2.0 solve this problem? Will the project scale to support the huge number of games being developed with decentralized Finance (DeFi) and blockchain? That’s what he decides.
The deployment of Ethereum 2.0 is currently being tested using Medalla Testnet, a multi-client test involving more than 20,000 validators worldwide. This is the last official public test before the deployment of Ethereum 2.0 Phase 0.
The current status of the project
As of September 2020, a “final” test network for the update called “Medalla”has been deployed. Unlike other previous test networks, this test is open to the public and will allow any of 5 clients-Prysm Prysmatic Labs, Lodestar ChainSafe, Teku PegaSys, Nimbus Status and Lighthouse Sigma Prime to connect to the network and communicate with each other. Also, because it is publicly available, network validators are not centrally coordinated by development teams. At the moment, more than 30,000 validators have joined the network, and more than 946,000 ETH have been placed on them.
The test is expected to last until the end of this year, after which Ethereum 2.0 Phase0 will be officially deployed (main network). The Main ETH 2.0 network is currently expected to launch in November 2020. It is important to remember that its clients will not be developed by one party. Instead, it will have a robust ecosystem for developers, and 5 different versions of clients.
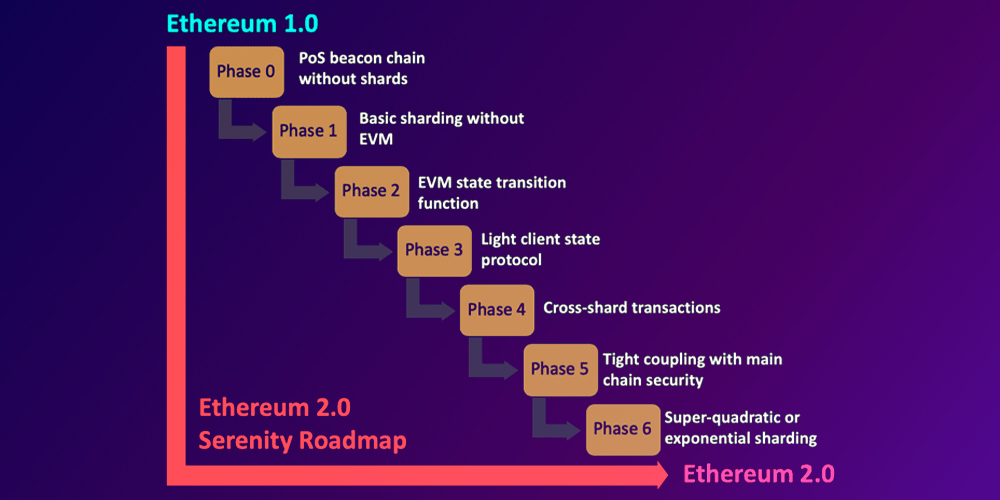
Ethereum 2.0 roadmap
So, based on the roadmap diagram above, Ethereum 2.0 is running at stage 0. Acceptance to the test network was overwhelming: more than 20,000 validators registered and directed their resources to help in the Beacon Chain test network. Vitalik Buterin, the founder of Ethereum, said that this will not be the “final” test of the Beacon Chain, so we should expect even more community involvement in the coming months.
As you can see in the diagram below, the first “layer” of the Ethereum 2.0 architecture, i.e. the Beacon Chain, is currently being tested. In the coming months, the current phase 0-Beacon Chain will be completed, and development will move on to build phase 1-Shard Chain and finally phase 2-Execution Engine.
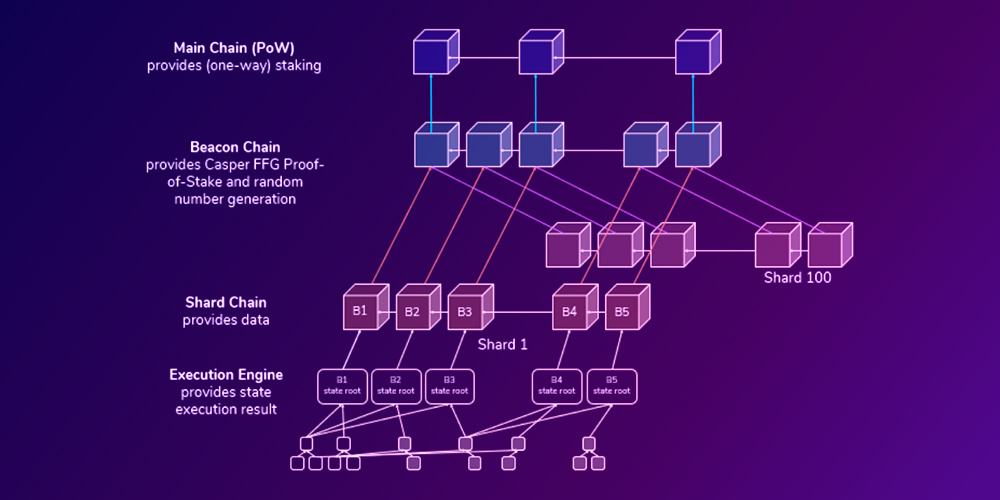
The entire upgrade consists of stages:
- Phase 0: a Chain of beacons
The goal of stage 0 is to provide validation and randomness for a block of segments. With the launch of Phase 0, a new ETH2 token appears. Users will be able to convert to ETH2 (in a 1: 1 ratio) through a registration agreement that effectively burns the ETH used for storage. The community will be able to put 32 ETH2 on validator nodes.
- Phase 1: Shard Chain
Phase 1 will allow Ethereum to scale immeasurably with shards. The network will be divided into 64 shards that work simultaneously, meaning they will all process transactions and calculations. Stage 1 will also allow shards to communicate with each other through cross-references.
- Phrase 2: The Implementation Mechanism
Phase 2 will lead to the final form of Ethereum 2.0. This is when an existing proof of work (outdated) and a new proof-of-stake network are combined. From now on, ETH will be merged with ETH2 and a new era for Ethereum will begin.
Awards for stacking
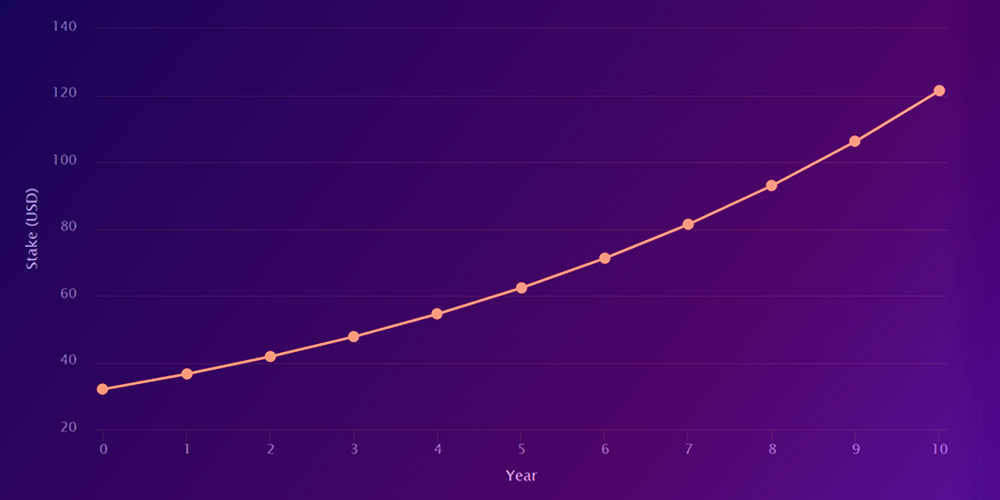
Ethereum 2.0 will switch to the Proof of Stak consensus-proof of ownership. Above, in the paragraph “Phase 0-Beacon Chain”, we mentioned that 32 ETH can be placed by the community on validator nodes. 32 ETH2 bids are used to verify transactions and network States, and also serve as a guarantee that the validator node will be honest and functional. In return, those who place a bet will be rewarded with new coins for their efforts. This means that validators will generate Ethereum as passive income and gradually receive payments in ETH.
Current rate calculations show an annual return on investment (ROI) of 14.2%. This will be great for those who will use ETH stacking, who can enjoy the benefits of passive income by personally storing their funds on the validator node. Analysts predict an increase in demand for ETH after the introduction of proof of stake due to additional demand for the asset from the stacking nodes and validator, while at the same time reduced demand for GPUs, as Ether mining will eventually be discontinued.
Conclusion
Ethereum is one of the most significant projects in the crypto space, and many other projects depend on it. It has excellent support from the developer community as well as businesses. There are many parties invested in the future of this blockchain, and the pressure for success is high.
If the team manages to do this, we will have a fully scalable General-purpose blockchain that will be closer to the initial step – the “World supercomputer”. It will also show the world that the dream of a perfect blockchain is possible. This will attract even more developers and investors to continue creating amazing projects based on universal blockchains.
Frequently asked questions (FAQ)
- Can you withdraw ETH2 back to regular ETH?
At stage 0, ETH2 cannot be withdrawn back to normal ETH. After conversion, ETH2 can only be used in the betting chain until phase 3.
- Can I lose my ETH Deposit on a node?
Yes. The 32 ETH bid for the validator node is designed to ensure that the validator node is always running and online. If the node is disabled, penalties will be imposed, and small amounts of ETH will be debited over time.
- When will the mining of the Ether
Mining is not over yet. Ethereum will keep mining in the main chain until at least the end of 2020. The main ETH1 chain will continue to use mining and work in parallel with the ETH 2.0 chain. This is necessary to ensure stability during migration.


